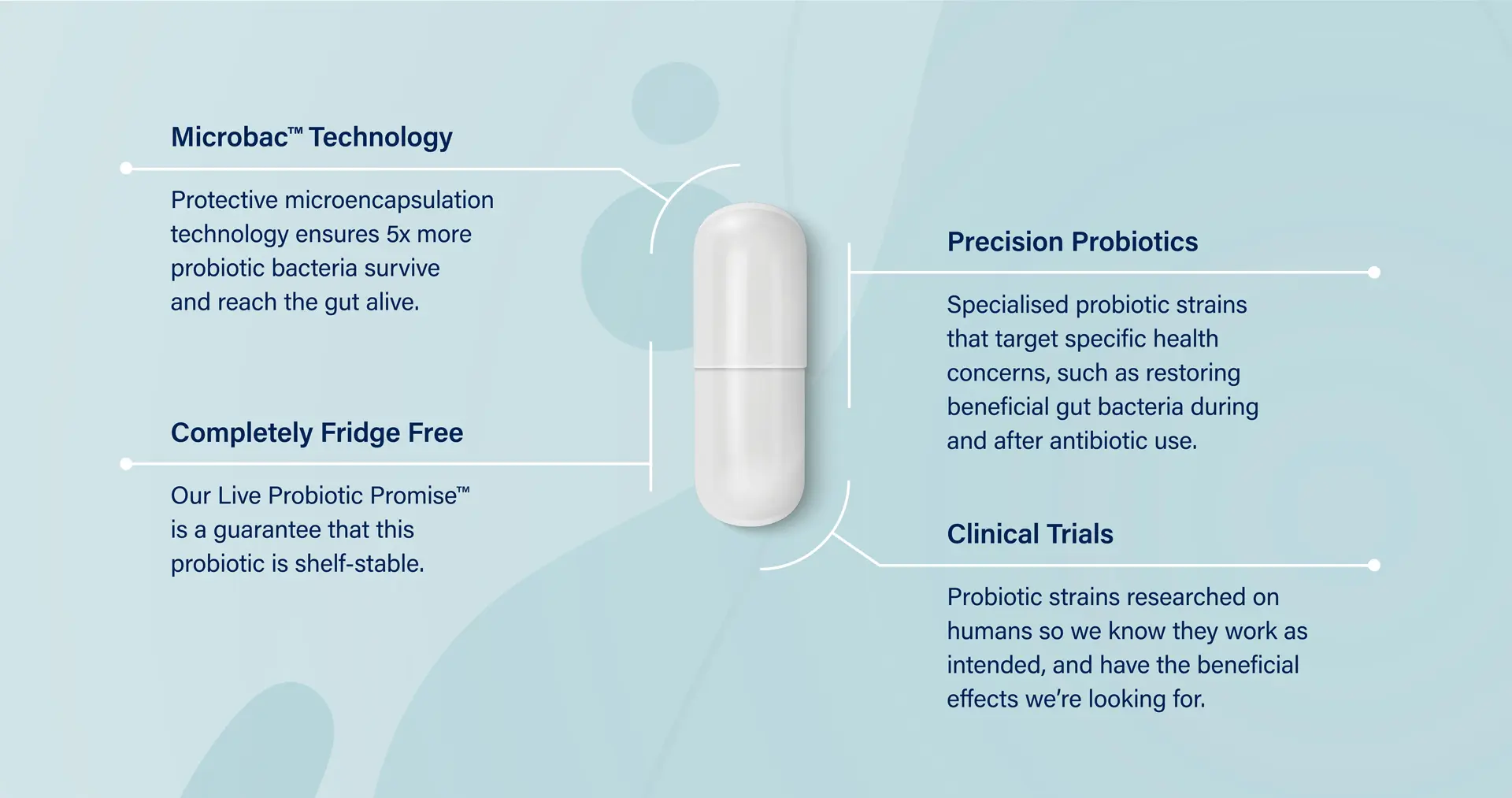
Description
Benefits
Biome Advanced™ Probiotic:
- Supports beneficial gut bacteria during antibiotic use
- Helps restore beneficial gut bacteria after antibiotic use
- Promotes healthy digestion and bowel regularity
Features
Shelf-stable; refrigeration not required
No added:
GMOs | wheat | gluten | dairy | lactose | fructose | yeast | nuts | seeds | peanut | soy | egg | fish | shellfish | animal derivatives
No artificial colours, flavours, sweeteners, or preservatives.
Suitable for vegetarians and vegans
Active Ingredients
| Each capsule contains: | |
| Lactobacillus plantarum6595 (DSM 6595) | 9 BLB* |
| Lactobacillus plantarum HEAL9 (DSM 15312) | 0.5 BLB* |
| Lactobacillus paracasei 8700:2 (DSM 13434) | 0.5 BLB* |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103) | 5 BLB* |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus LA02 (DSM 21717) | 5 BLB* |
| Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BS01 (LMG P-21384) | 10 BLB* |
| Total live bacteria | 30 BLB* |
|
*BLB = Billion Live Bacteria |
Directions
Adults and children over 12 years: Take 1 capsule daily (with or without food), or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.Biome Advanced™ Probioticis recommended daily during antibiotic use, starting on the first day of the course. Continue taking Biome Advanced™ Probiotic daily for at least two weeks after completing a course of antibiotics.
Always read the label. Follow the directions for use.
Science
Antibiotics are commonly used medicines in Australia to treat conditions caused by bacterial infections. While antibiotics are very effective in killing harmful bacteria, they also unintentionally target the good bacteria that live in the gut, disrupting the balance of bacteria which make up the gut microbiome. This disruption to the gut microbiome is known as ‘dysbiosis’, and can cause side effects such as diarrhoea(1). Taking probiotics during and after antibiotic use can help to restore the number and diversity of beneficial bacteria in the gut(2), keeping the digestive system healthy.
References
- McFarland LV. Epidemiology, risk factors and treatments for antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Dig Dis Basel Switz. 1998 Oct;16(5):292–307.
- Engelbrektson A, Korzenik JR, Pittler A, Sanders ME, Klaenhammer TR, Leyer G, et al. Probiotics to minimize the disruption of faecal microbiota in healthy subjects undergoing antibiotic therapy. J Med Microbiol. 2009 May 1;58(5):663–70.